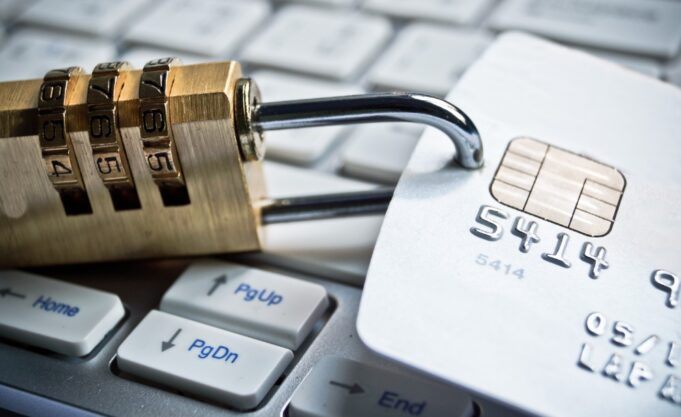
As cybercrime is on the rise, secure payment options become imperative for businesses. This extends across various sectors of the digital economy, from e-commerce to online services.
Here we take a look at the importance of secure payments, the key cybersecurity features and best practises.
Evolution of Payment Methods
The landscape of payments has evolved significantly over the years, from cash-based to cards, to digital platforms. This has been largely driven by emerging technology and shifting consumer preferences.
Since the 10th century, paper money was the primary way of payments. This has been replaced by banknotes, and later by checks and bank cards in the 20th century. More recently, electronic payment methods like online banking, digital wallets, and mobile payment applications, have become commonplace.
The growth of e-commerce has been a significant catalyst in the development of new payment methods. Online shopping requires payment solutions that are secure, convenient and fast. Digital wallets like ApplePay and GooglePay, emerged as the winner. They are now the most popular payment method worldwide, followed by cards. In 2022, digital wallets amounted to 49% of all online ransactions.
Security Challenges in Digital Payments
As digital payment methods become more prevalent, they also become targets for cybercriminals. Security challenges in this domain are continuously evolving.
IT Governance found there were 1,064 security incidents in 2022, resulting in 480,014,323 data breaches. Meanwhile, in 2020, in the midst of the Covid-19 pandemic, more than $1tn was lost due to cybercrime.
Online payment systems are susceptible to various cybersecurity threats. The most common include phishing, identity theft, account takeover, spoofing and authorised push payment fraud (APP). In the UK alone, APP fraud losses amounted to £293,3m in the first half of 2023, with £42.6m of it being business losses.
Fraudulent activities and unauthorised transactions pose significant risks in the digital payment landscape. Effective security measures are essential to detect and prevent such activities, ensuring the safety of both merchants and customers.
Technologies Enhancing Payment Security
Technology plays a crucial role in enhancing payment security. Below are the key cybersecurity features used by payment service providers to minimise the risks.
Encryption
Encryption is like turning a message into a secret code. It protects sensitive information during transmission, so only the authorised person with a key can read it. This keeps data safe from cybercriminals. Encryption is a fundamental technology employed in the modern payment ecosystem.
Tokenisation
Tokenisation in payments swapping your real card information with a unique token. The tokens cannot be reverse-engineered and therefore are useless to hackers. When a customer makes online purchases, the token is sent instead of their real card number, keeping your the details hidden and secure.
Multi-Factor Authentication
Multi-factor authentication (MFA) requires users to verify identity using more than one factor. These factors and they include:
- Knowledge: Something they know, like a password or a PIN.
- Possession: Something they have, lie a smartphone or a security token. It’s a physical item that can generate or receive a code.
- Inherence: Something they are, like a fingerprint or face scan. This is called biometric verification.
MFA is widely used in online transactions to autorise online payments. For example, strong customer authentication (SCA), which includes some elements of MFA, is a legal requirement under the European PSD2 regulation.
Regulatory Compliance
Regulatory compliance plays a significant role in ensuring the security of online payment systems. Adhering to standards and regulations is essential for maintaining a secure environment for digital transactions.
PCI DSS is an industry benchmark. It is a set of security standards designed to ensure that all companies that accept, process, store, or transmit card information maintain a secure environment.
GDPR regulates how companies protect the personal data and privacy of individuals within the European Union. This directly impacts how online payments are processed and secured.
Best Practices for Secure Online Payments
Adopting best practices for secure online payments is crucial for both businesses and consumers. These can help mitigate risks and protect against potential security breaches.
Keeping software and payment systems updated is vital in protecting against the latest security threats. Regular updates often include patches for newly discovered vulnerabilities.
Meanwhile, using secure network connections, such as Virtual Private Networks (VPNs), especially when conducting transactions over public Wi-Fi, can greatly enhance security.
Additionally, raising awareness about secure online payment practices is essential. Educating consumers and employees on how to recognise fraudulent activities can prevent potential risks.
Future of Secure Digital Payments
The future of digital payments is likely to see continued innovation and development, with a focus on enhancing security and user experience.
Technologies like blockchain, biometric authentication, artificial intelligence, and open banking are expected to play significant roles.
The trend towards contactless payments using Near Field Communication (NFC) technology, is expected to continue growing. Contactless payments became especially popular after the Covid-19 pandemic.
Secure payment options are fundamental to the success and sustainability of the digital economy. As the landscape continues to evolve, the focus on security will remain paramount.