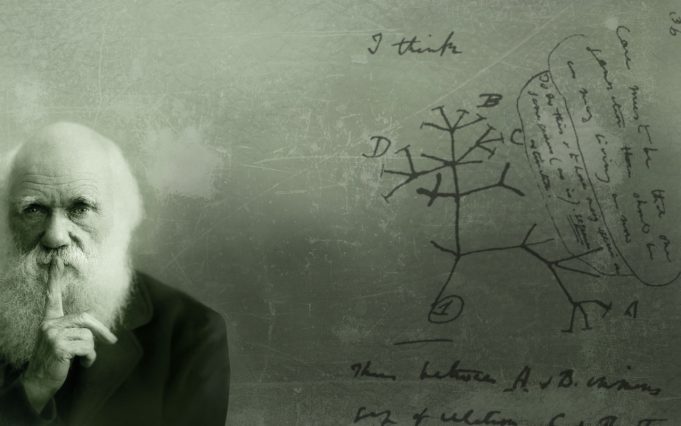
Throughout history, many new scientific theories have shaken up common religious beliefs, including Charles Darwin’s Theory of Evolution. In 1831, 22-year-old Darwin accompanied Captain Robert Fitzroy on the HMS Beagle, around Argentina, Australia and Cape Town and eventually the Galapagos Islands where the amateur naturalist spent 5 weeks collecting fossils and samples from the island and began to develop his evolutionary theory.
In 1858, Darwin received a paper written by Alfred Russel Wallace that held the same views and theories as his own work, but he refused to publish his paper just to beat Wallace to the punch. Instead, he collaborated with Wallace and published a paper, which was presented at the Linnean Society of London. A debate was held after this publication in which several speakers from religious and scientific backgrounds expressed their opinions (The Voyage of the Beagle, BBC).
The Evidence
There is evidence that supports Darwin’s theories, such as vestigial organs, fossil records and homology (similarity based on common descent). The hair follicles on human skin indicate that humans are descended from a much hairier species, as does the vestigial tail, known as the coccyx but often referred to as the tailbone.
Fossil records going far back in history show evidence of change as well as extinctions, proving those extinct species to be relatives of living species. The similarity on vertebrate forelimb structure, even though function may be quite different, and similarities in genetic codes are indicators of a common ancestor.
The Controversy
Adapted from The American Museum of Natural History is this Controversy Timeline, which is of much interest:
- 1749-1844: There were naturalists and evolutionists before Darwin’s time, but none could explain how we evolved.
- 1802: Theologist William Paley came up with the idea that all complex organisms had to have been made by a creator.
- 1859: Origin of the Species is published.
- 1860: The debate where the Bishop of Oxford, Samuel Wilberforce attacked Darwin’s theories. Fellow scientists Thomas Huxley and Joseph Hooker defended Darwin.
- 1871: The Descent of Man is published applying evolution to humans.
- 1850’s-1920: Social Darwinism began, applying survival of the fittest in human circles, where people wanted governments to allow the ‘fit’ to be successful and allow the ‘unfit’ to decline.
- 1882: Darwin’s death.
- 1925: The Scopes ‘Monkey Trial’, where a biology teacher is tried for violating the law in Tennessee, that stated public teachers weren’t allowed to teach evolution.
- 1948: The U.S. Supreme Court bans religious teachings in public schools.
- 1960: Evolution taught in schools.
- 1981: The ideas of intelligent design and creationism are formed.
- 1996: Pope John Paul II states that there is no contradiction between evolutionary science and Catholicism.
- 2000-2002: Polls reveal that 57% of Americans believe in creationism.
- 2004: Parents in Pennsylvania challenge the school board in regards to trying to teach intelligent design as an alternative to Evolution.
- 2009: Darwin Bicentennial.
Humans and chimpanzees share almost 99% of DNA and it is believed the divergence on the evolutionary tree was as little as 5–6 million years ago, suggesting that chimpanzees, not apes, are humans’ closest living relatives. Continued studies of ape and chimpanzee genomes will assist scientists in figuring out exactly where humans fit in, but there is no doubt, the debate will continue.